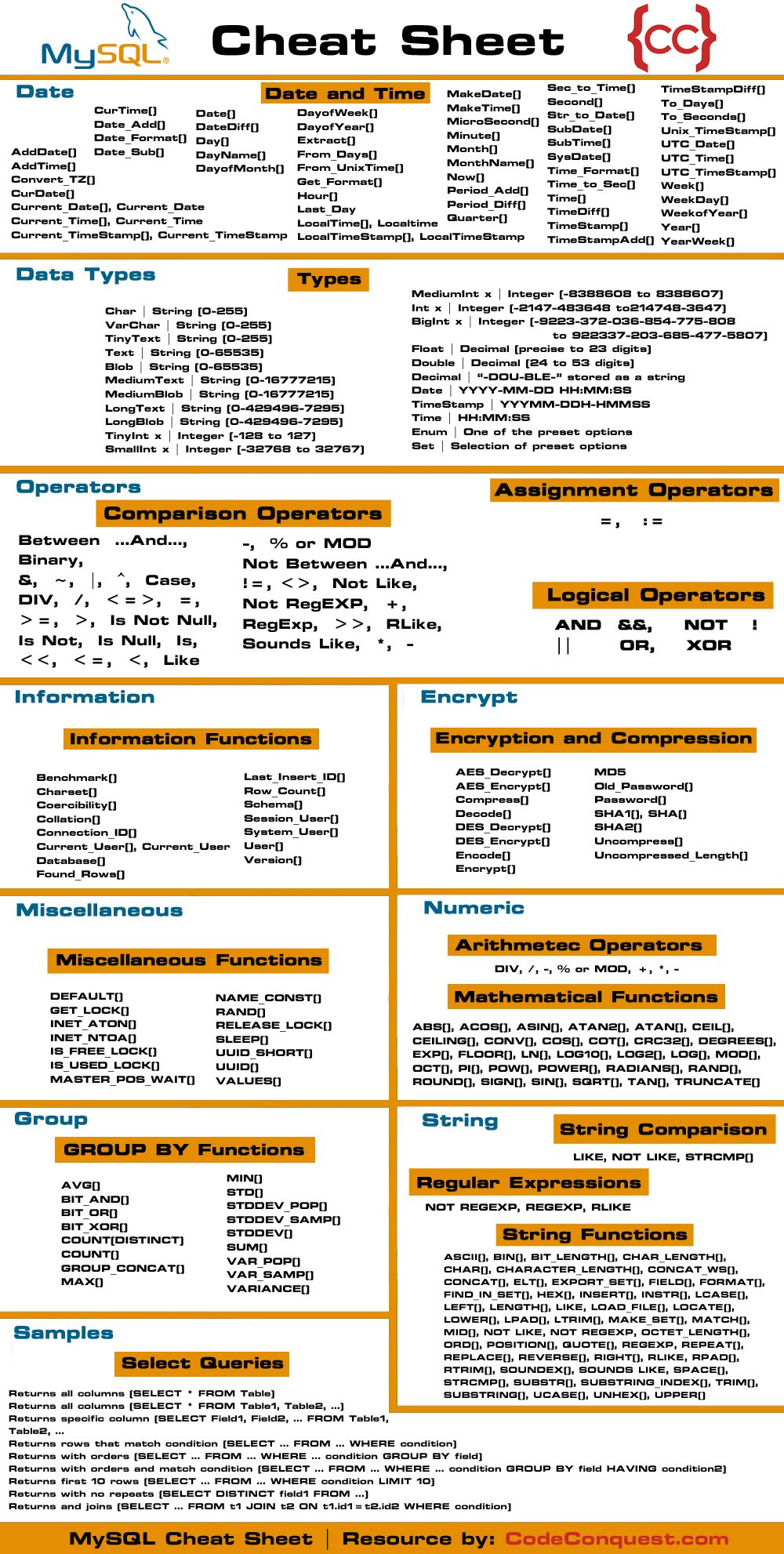
Xdebug phpstorm chrome. The SQL cheat sheet provides you with the most commonly used SQL statements for your reference. You can download the SQL cheat sheet as follows:
Our SQL Cheat Sheet enables you to revise almost the entire set of SQL Commands quickly. It is highly recommended to go through this cheat sheet if you are: Preparing for your SQL exam Going for an interview. Queries First log in as root and use the mysql database: mysql -uroot -p mysql (password is prompted). Don't forget that every query must be terminated with; In the overview below, CAPITALIZED words are part of the SQL syntax, lowercase words are names of tables, columns, etc.
Querying data from a table
Query data in columns c1, c2 from a table
Query all rows and columns from a table
Query data and filter rows with a condition
Query distinct rows from a table
Sort the result set in ascending or descending order
Skip offset of rows and return the next n rows
Group rows using an aggregate function
Filter groups using HAVING clause
Querying from multiple tables
Mysql Query Cheat Sheet Free
Inner join t1 and t2
Left join t1 and t1
Right join t1 and t2
Perform full outer join
Produce a Cartesian product of rows in tables
Another way to perform cross join
Join t1 to itself using INNER JOIN clause
Using SQL Operators
Combine rows from two queries
Mysql Query Download
Return the intersection of two queries
Subtract a result set from another result set
Query rows using pattern matching %, _
Query rows in a list
Query rows between two values
Check if values in a table is NULL or not
Managing tables
Create a new table with three columns
Delete the table from the database
Add a new column to the table
Drop column c from the table
Add a constraint
Drop a constraint
Rename a table from t1 to t2
Rename column c1 to c2
Remove all data in a table
Using SQL constraints
Set c1 and c2 as a primary key
Set c2 column as a foreign key
Make the values in c1 and c2 unique
Ensure c1 > 0 and values in c1 >= c2
Set values in c2 column not NULL
Modifying Data
Insert one row into a table
Insert multiple rows into a table
Insert rows from t2 into t1
Update new value in the column c1 for all rows
Update values in the column c1, c2 that match the condition
Sql Query Cheat Sheet Pdf
Delete all data in a table
Delete subset of rows in a table
Managing Views
Create a new view that consists of c1 and c2
Create a new view with check option
Create a recursive view
Create a temporary view
Mysql Query Cheat Sheet Pdf
Delete a view
Managing indexes
Create an index on c1 and c2 of the t table
Create a unique index on c3, c4 of the t table
Drop an index
Managing triggers
Create or modify a trigger
WHEN
- BEFORE – invoke before the event occurs
- AFTER – invoke after the event occurs
EVENT
- INSERT – invoke for INSERT
- UPDATE – invoke for UPDATE
- DELETE – invoke for DELETE
TRIGGER_TYPE
- FOR EACH ROW
- FOR EACH STATEMENT
Delete a specific trigger
A query is a command used to interact with a database. When you interact with a MySQL database, queries are written in the SQL language.
Below are all of the common MySQL query commands as well as examples of common queries.
Common query functions
SELECT— used to retrieve objects from a database tableINSERT— used to insert new objects into a database tableUPDATE— used to update existing objects in a database tableDELETE— used to delete objects from a database tableFROM— used to specify the database table you wish to interact withWHERE— used to filter the objects retrieved based on specified criteriaLIMIT— used to restrict the number of objects retrieved via a queryLIKE— used to perform string comparisons; the%wildcard matches any number of characters, even zero characters; e.g. to select animals whosetypecontains 'wolf', you could useSELECT * FROM animals WHERE type LIKE '%wolf%'
Queries to Select, Insert, Update, and Delete objects in a MySQL database
Mysql Query Cheat Sheet Printable

Say, for example, you have a database table, cars, with the following columns:
Mysql Query Tutorial
Filter groups using HAVING clause
Querying from multiple tables
Mysql Query Cheat Sheet Free
Inner join t1 and t2
Left join t1 and t1
Right join t1 and t2
Perform full outer join
Produce a Cartesian product of rows in tables
Another way to perform cross join
Join t1 to itself using INNER JOIN clause
Using SQL Operators
Combine rows from two queries
Mysql Query Download
Return the intersection of two queries
Subtract a result set from another result set
Query rows using pattern matching %, _
Query rows in a list
Query rows between two values
Check if values in a table is NULL or not
Managing tables
Create a new table with three columns
Delete the table from the database
Add a new column to the table
Drop column c from the table
Add a constraint
Drop a constraint
Rename a table from t1 to t2
Rename column c1 to c2
Remove all data in a table
Using SQL constraints
Set c1 and c2 as a primary key
Set c2 column as a foreign key
Make the values in c1 and c2 unique
Ensure c1 > 0 and values in c1 >= c2
Set values in c2 column not NULL
Modifying Data
Insert one row into a table
Insert multiple rows into a table
Insert rows from t2 into t1
Update new value in the column c1 for all rows
Update values in the column c1, c2 that match the condition
Sql Query Cheat Sheet Pdf
Delete all data in a table
Delete subset of rows in a table
Managing Views
Create a new view that consists of c1 and c2
Create a new view with check option
Create a recursive view
Create a temporary view
Mysql Query Cheat Sheet Pdf
Delete a view
Managing indexes
Create an index on c1 and c2 of the t table
Create a unique index on c3, c4 of the t table
Drop an index
Managing triggers
Create or modify a trigger
WHEN
- BEFORE – invoke before the event occurs
- AFTER – invoke after the event occurs
EVENT
- INSERT – invoke for INSERT
- UPDATE – invoke for UPDATE
- DELETE – invoke for DELETE
TRIGGER_TYPE
- FOR EACH ROW
- FOR EACH STATEMENT
Delete a specific trigger
A query is a command used to interact with a database. When you interact with a MySQL database, queries are written in the SQL language.
Below are all of the common MySQL query commands as well as examples of common queries.
Common query functions
SELECT— used to retrieve objects from a database tableINSERT— used to insert new objects into a database tableUPDATE— used to update existing objects in a database tableDELETE— used to delete objects from a database tableFROM— used to specify the database table you wish to interact withWHERE— used to filter the objects retrieved based on specified criteriaLIMIT— used to restrict the number of objects retrieved via a queryLIKE— used to perform string comparisons; the%wildcard matches any number of characters, even zero characters; e.g. to select animals whosetypecontains 'wolf', you could useSELECT * FROM animals WHERE type LIKE '%wolf%'
Queries to Select, Insert, Update, and Delete objects in a MySQL database
Mysql Query Cheat Sheet Printable
Say, for example, you have a database table, cars, with the following columns:
Mysql Query Tutorial
make— aVARCHARcolumn with the brand/company that made the carmodel— aVARCHARcolumn with the car's modelyear— aYEARcolumn with the year the car was made
